The Arctic archipelago of Svalbard is one of the northernmost parts of the world, and in a both harsh and lovely climate, people have been attracted to the island the recent centuries for hunting, whaling, coalmining, research and the magnificent scenery. All of this is something you can experience while visiting the northernly places with a few town and great nature.
Norwegian Longyearbyen and Russian Barentsburg are the two largest urban communities in Svalbard. They are located at a distance that often makes tourists visit both places during a stay on the islands. The sea route between the towns is an journey through the vast nature and with a look to both historical mining communities and glaciers.
Longyearbyen, like so many other places in Svalbard, started out as a mining town, but today it has much else to offer tourists. Shops, restaurants, a museum and many excursions are available. For many, Longyearbyen also serves as the site for the main stay in Svalbard, although there is also a hotel in Barentsburg.
A special time is in the summer when the sun shines around the clock for several months, and the midnight sun is an impressive experience. Equally impressive is the Northern Lights that prevail in the dark, long winter. In that way, Svalbard has several seasons and has something to offer anyone looking for a secluded destination with special sights and activities.
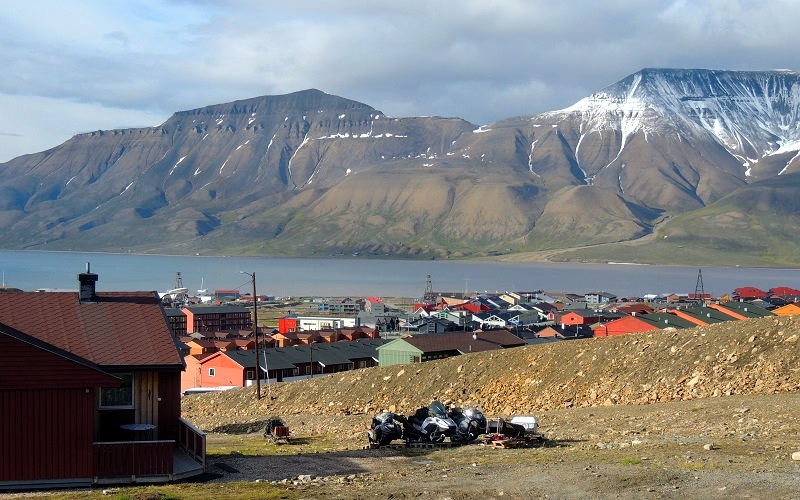

With about 2,000 inhabitants, Longyearbyen is the largest settlement in Svalbard, and the city serves as the archipelago’s administrative and commercial center. You can go for shopping here, visit museums, the church and see the others sights in town.
The Svalbard Museum is an interesting museum where you can learn much more about Svalbard’s culture, history, nature and the research that takes place on and around the archipelago.
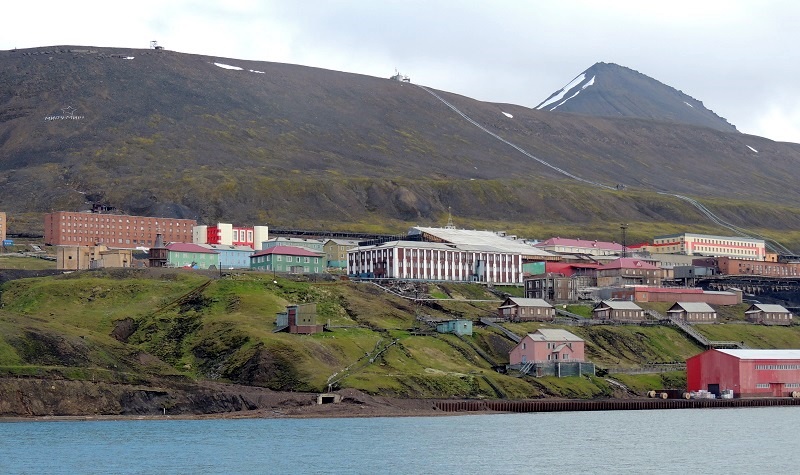

The town of Barentsburg is the second largest settlement in Svalbard. It was established in Green Harbor in 1920 and named after Dutch Willem Barents, who rediscovered the archipelago of Svalbard in 1596. Russian Arktikugol bought the mine in 1932, and it is today a Russian mining community.
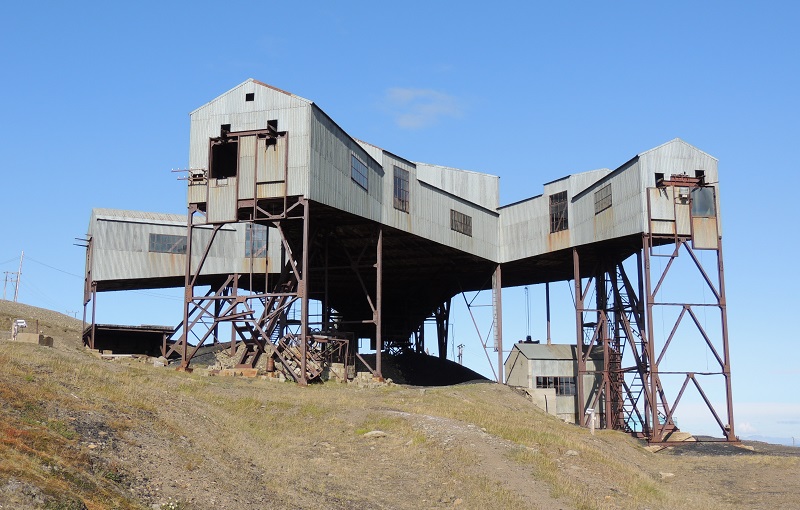

This construction is one of the most distinctive and characteristic buildings in Longyearbyen. During its operation, the junction served as a gathering point for the coal coming from various mines around the city.
At this fine museum you can explore the exciting and dramatic expeditions that, with airships, departed from Svalbard towards the North Pole. These are the ships America in 1906-1909, Norway in 1926 and Italy in 1928.
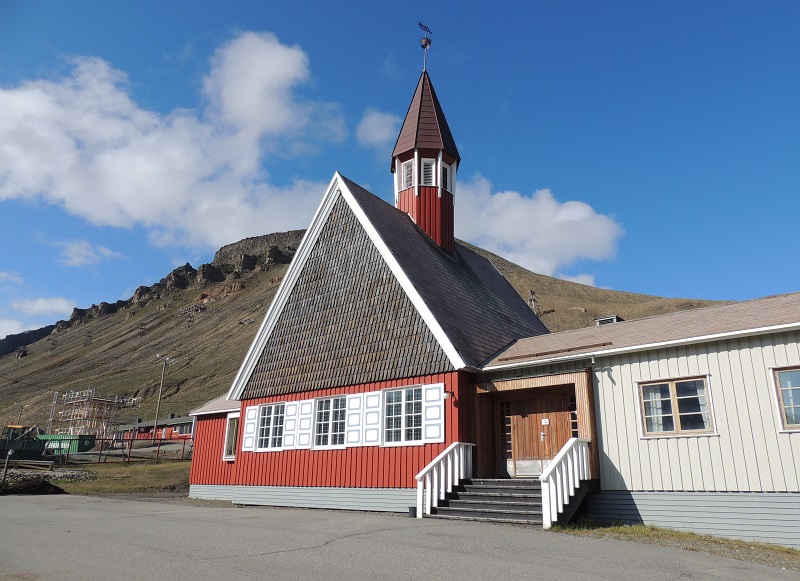

Svalbard Church was built and serves as a church for all residents of the archipelago, and people from, for example, Barentsburg and Sveagruva are also always welcome here. The present church was inaugurated in 1958.
The University Centre in Svalbard is a public university founded in 1993 by the Norwegian state. The idea of a university was to offer higher education in Arctic science.
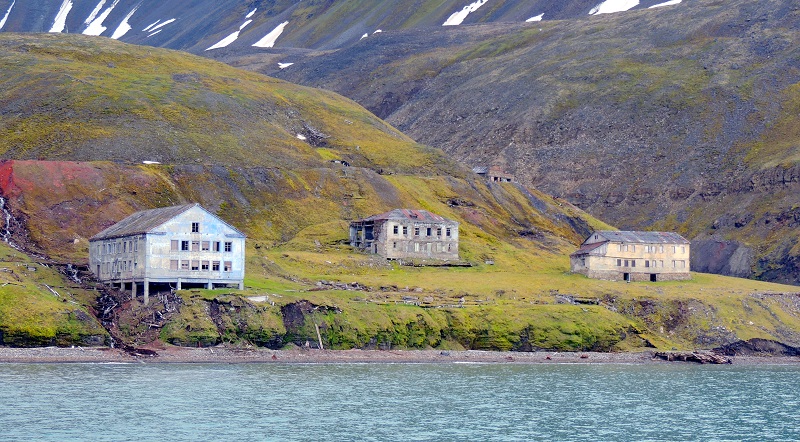

Grumant is the name of a former Soviet settlement that began its history around 1910. Grumant had a population of about 1,200 inhabitants and was thus a larger mining community. However, it was closed in 1961 due to declining production and difficult shipping conditions.
This is the last coal mine in operation around Longyearbyen. It is located in the area east of town. The drive to to mine is an attraction in itself with large wetlands and a flat land area between the mountains.
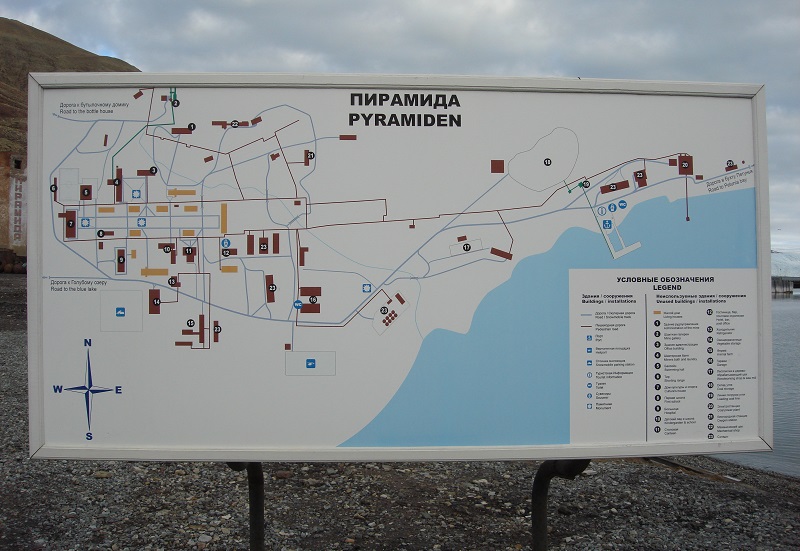
Pyramida is a former Russian mining community founded by Arktikugol/Арктикуголь in the same way as the present Barentsburg west of Longyearbyen. Arktikugol still owns the Pyramid, which can be visited as a historical site.
Hovedgaten
svalbardbutikken.no
Elvesletta
Main street
Spitsbergen Airship Museum
spitsbergenairshipmuseum.com
Svalbard Museum
svalbardmuseum.no
Henningsen Transport & Guiding
Sjøskrenten
htg.svalbard.no
Svalbard is believed to have been discovered by Scandinavians in the 1100s, and they called the archipelago Svalbarð, which means cold coasts. The name may also refer to parts of Greenland and the island of Jan Mayen, as the land was then considered to be continuous. The Scandinavians used Svalbard for hunting and fishing for some time.
Holland was one of the rich European powers of the 16th century, which through trade had created both solid revenues and an internationally oriented society. In 1596, the country introduced a reward to those who could find the Northeast passage north of Russia to Asia, and the Amsterdam City Council equipped two ships to conduct the experiment.
In mid-May 1596 Willem Barentz set out from the Dutch coasts. On June 10, the expedition came to the Bjørne Island, and on June 17 they gained land acquaintance with Spitsbergen, which they thereby rediscovered after centuries without human activity on the archipelago. Barentz and crews sailed around several fjords before sailing to the Bear Island in late June and on to the northeast, where Willem Barentz died on June 20, 1597, after surviving the winter on Novaja Zemlja.
The first hunting expeditions in the seas around Svalbard went to the Bear Island, to which the English Muscovy Company organized a trip in 1604. The target was a large colony of walruses which were locally eradicated after the following years.
From 1611, it was the whales around Spitsbergen that attracted interested fishing companies. The majority of English and Dutch whalers were present, but there were, for example, Spanish and French boats in the area. The Muscovy Company believed they had exclusive rights to the catches, and they sent armed boats to remove competitors.
The English aggression caused the Netherlands to declare the English right to void and the sea free, while the King of Denmark-Christian, Christian IV, regarded the area as belonging to his kingdom due to the geographical connection with not least the possession of Greenland. Thus, in 1615, Denmark-Norway sent tax collectors to foreign boats, which however paid off.
In 1614, England and the Netherlands had effectively divided Spitsbergen and the sea area between them, and the Dutch created the company Noordsche Companie for this purpose. After a few years, the English Muscovy Company got into financial difficulties, making the Netherlands dominant in the catchment areas. They settled on base in northwest Svalbard and allowed only a limited Danish presence. England was directed to the south, and French to the north coast and the open waters.
Formally, Denmark-Norway had not abandoned the claim for Svalbard, but the area nonetheless transitioned to a status of terra nullius; a country under no sovereignty.
The Dutch base was Smeerenburg on the island of Amsterdam Island. It was home to about 200 employees. The total activities in and around Svalbard were increased through the 1600s to a total of about 10,000 people and up to 300 ships.
Gradually, whaling moved from land to sea. Instead of the fjords, it became the open sea and the pelagic zone that, with the development of technology, became an increasingly important part of the activities, and with it many of the settlements disappeared.
The whaling lasted into the 18th century, when the Dutch continually downsized the activities to completely abandon the whaling around the archipelago in 1770. The English moved their fishing boats to other areas in the early part of the following century.
During the same time, hunting other than the whaling took place. To a lesser extent, polar bears, seals and polar foxes were hunted.
The geographical exploration of Svalbard started in earnest around 1610, when the developing whaling sought new areas.
In the middle of the century, it was found that Spitsbergen was an island and that Svalbard was not associated with Greenland, as would otherwise be assumed.
It was the coastlines and the sea area that were the focus of the expeditions, and thus the interior of the islands remained unknown for many years.
Scientific expeditions were started by Russia on a 1764-1766 voyage, and this type of exploration was followed by, among others, Norway, France, England and Sweden over the years. Among the well-known expeditions are the Swedes Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld and Otto Torell’s two tours in the 1860s.
Svalbard has many times in history been the starting point for exploration trips to the North Pole. With the location close to the top of the Earth, the northwest of Spitsbergen has been the basis for some of these journeys.
Several attempts to reach the North Pole itself were tried from the end of the 19th century. This happened, among other things, in hot air balloons and in airships, of which the ship Norway with Roald Amundsen as expedition leader succeeded with his presence in 1926. Two years later, Italian Umberto Nobile the airship Italy flew on several voyages. On one trip, however, things went wrong and the airship crashed.
In the late 1800s, interest in Svalbard’s raw materials started in the form of permanent settlements and mining.
First was Swedish Alfred Gabriel Nathorst, who in 1872 established Kapp Thordsen as the base for the mining of phosphorite. However, the plan was not implemented and instead it became the coal that led to the first industrial mining on the archipelago.
In 1899, Søren Zachariassen from Tromsø started mining coal in the Ice Fjord, and he exported coal from Svalbard for a few years. In 1901, the Bergen-Spitsbergen Kullgrube Company began breaking coal at the Advent summit, and the first year’s result was 5 tonnes of coal, which they transported to their boat by rowboat.
In 1896, the shipping company Vesteraalen’s Steamship Company started to sail tourists to Hotellneset, which is located at the present airport at Svalbard. A prefabricated hotel was set up while tours were not profitable and was therefore stopped after the opening season.
On a later tourist trip, John Munroe visited Longyear in Svalbard in 1901, and he spoke with an expedition searching for coal. Longyear returned to the archipelago in 1903, and he ended up buying the mining rights on the west side of the Advent Fjord, and subsequently expanded the area considerably.
In 1906, the American Arctic Coal Company started with John Munroe Longyear at the forefront of mine 1a after establishing houses and docks. The town was called Longyear City, and the coal was broken 1.2 kilometers from the harbor, to which it was added by cable car.
Elsewhere on Spitsbergen, mines were also established during this period. Sweden opened the Svea mine and the Pyramid, while the Dutch established Barentsburg. The last two were later purchased by the Soviet Union. In 1916, the Norwegian Kings Bay Coal Company opened activities in Ny-Ålesund to increase self-sufficiency with coal.
Arctic Coal Company had financial difficulties in connection with World War I, and their activities were purchased by Store Norske, who later renamed Longyear City to Longyearbyen.
Store Norske built new houses, furnished hospital and on the whole started the development of the actual town Longyearbyen is today. In 1920 the first pastor and teacher was appointed, and the following year, Svalbard Church was consecrated.
Tourism also began to develop after the first growth in Longyearbyen. In 1935, the steamship SS Lyngen began sailing to Longyearbyen with tourists during the summer season.
Norway was thus dominant in many ways on the archipelago, and so were those who, from 1907, took the initiative to settle the statelessness and lack of legislation that prevailed on Svalbard.
Here the country took steps towards negotiations between all the countries involved in activities on Svalbard, and it came to international conferences in 1910, 1912 and 1914.
The breakthrough came after World War I at the 1919 peace talks in Paris. This resulted in the Svalbard Treaty, signed on February 9, 1920 by a number of countries; however, with Russia / Soviet Union as a significant exception. Only Norway and Russia had a connection with Svalbard based on the natural geography. However, the Soviet Union signed an agreement in 1924.
With the Svalbard Treaty, the archipelago became part of the Kingdom of Norway; however, with significant exceptions. Taxation must only be done to maintain the administration in Svalbard, and therefore no transfers to the rest of Norway can be made from here. Environmentally, Norway is committed to preserving and protecting the nature of Svalbard. Citizens from all signatory countries must stay in Svalbard, and Norway must not discriminate between them. Similarly, the same countries must conduct trade, mining and other industries without obstacles other than the protection of nature. Military must not fortify Svalbard in Norway.
Germany occupied Norway in 1940, but Svalbard remained himself in that regard. There was talk of letting the archipelago be occupied by Soviet and British troops, but it opposed the Norwegian exile government.
Instead, the English evacuated Spitsbergen. On August 29, all inhabitants of the settlement Ny-Ålesund were moved to Longyearbyen, and on September 3, 765 people were sailed from there to Scotland. Later, several were evacuated.
The Germans established a runway and a smaller garrison, which served primarily as a weather service. They withdrew without a fight, after British forces later entered Barentsburg with the goal of securing Spitsbergen’s rich coal mines.
In 1943, Germany’s Kriegsmarine sent battleships Tirpitz and Scharnhorst as well as nine destroyers to Svalbard to bomb Longyearbyen, Grumant and Barentsburg. The operation was successful and only four houses remained in Longyearbyen, which remained unpopulated until 1945.
In 1944, the Soviet Union proposed that Svalbard be transformed into a condominium under shared Norwegian and Soviet rule, but this was rejected in 1947.
Norwegian reconstruction and restoration of production started in 1945, while the Soviet Union began its renewed activities from 1946. After a few years, the production from the mines was on par with the previous ones.
When Norway joined NATO in 1949, the Soviet Union protested that the Defense Alliance could not exert military influence on Svalbard, but this case was abandoned. Norway, on the other hand, was careful not to create unnecessary provocations; for example, the construction of an airport at Ny-Ålesund was rejected for this reason.
However, the need for the construction of an airport became more evident as the years went by. In 1971, a compromise was reached between Norway and the Soviet Union on the construction of the airport at Longyearbyen. It opened in 1975 as an airport for both Norwegian and Soviet communities, with Barentsburg southwest of Longyearbyen clearly dominating.
Longyearbyen and Svalbard have become a more ordinary society today than mining communities in the past, run by mining companies.
Thus, in the 1970s, Longyearbyen transitioned to a changed government, starting with the establishment of a city council in 1971. At its beginning, however, the council had only the authority to comment on proposals. Since 2002, the City Council has had many of the same powers and duties as other Norwegian City Councils.
Research and tourism have become a more important part of Svalbard’s economy, which in the past was almost entirely dependent on mining. From the 1990s hotels opened, and with Longyearbyen as the archipelago’s main city and tourist center, many activities have been developed. Best known are the boat trips that bring visitors to the still active Russian community in Barentsburg and to the former mining town of Pyramid.
Overview of Svalbard
The Arctic archipelago of Svalbard is one of the northernmost parts of the world, and in a both harsh and lovely climate, people have been attracted to the island the recent centuries for hunting, whaling, coalmining, research and the magnificent scenery. All of this is something you can experience while visiting the northernly places with a few town and great nature.
Norwegian Longyearbyen and Russian Barentsburg are the two largest urban communities in Svalbard. They are located at a distance that often makes tourists visit both places during a stay on the islands. The sea route between the towns is an journey through the vast nature and with a look to both historical mining communities and glaciers.
About the upcoming Svalbard travel guide
About the travel guide
The Svalbard travel guide gives you an overview of the sights and activities of the Norwegian city. Read about top sights and other sights, and get a tour guide with tour suggestions and detailed descriptions of all the city’s most important churches, monuments, mansions, museums, etc.
Svalbard is waiting for you, and at vamados.com you can also find cheap flights and great deals on hotels for your trip. You just select your travel dates and then you get flight and accommodation suggestions in and around the city.
Read more about Svalbard and Norway
Buy the travel guide
Click the “Add to Cart” button to purchase the travel guide. After that you will come to the payment, where you enter the purchase and payment information. Upon payment of the travel guide, you will immediately receive a receipt with a link to download your purchase. You can download the travel guide immediately or use the download link in the email later.
Use the travel guide
When you buy the travel guide to Svalbard you get the book online so you can have it on your phone, tablet or computer – and of course you can choose to print it. Use the maps and tour suggestions and you will have a good and content-rich journey.
Longyearbyen • Barentsburg • Polar Bears • Glaciers • Midnight Sun
Overview of Svalbard
The Arctic archipelago of Svalbard is one of the northernmost parts of the world, and in a both harsh and lovely climate, people have been attracted to the island the recent centuries for hunting, whaling, coalmining, research and the magnificent scenery. All of this is something you can experience while visiting the northernly places with a few town and great nature.
Norwegian Longyearbyen and Russian Barentsburg are the two largest urban communities in Svalbard. They are located at a distance that often makes tourists visit both places during a stay on the islands. The sea route between the towns is an journey through the vast nature and with a look to both historical mining communities and glaciers.
About the upcoming Svalbard travel guide
About the travel guide
The Svalbard travel guide gives you an overview of the sights and activities of the Norwegian city. Read about top sights and other sights, and get a tour guide with tour suggestions and detailed descriptions of all the city’s most important churches, monuments, mansions, museums, etc.
Svalbard is waiting for you, and at vamados.com you can also find cheap flights and great deals on hotels for your trip. You just select your travel dates and then you get flight and accommodation suggestions in and around the city.
Read more about Svalbard and Norway
Buy the travel guide
Click the “Add to Cart” button to purchase the travel guide. After that you will come to the payment, where you enter the purchase and payment information. Upon payment of the travel guide, you will immediately receive a receipt with a link to download your purchase. You can download the travel guide immediately or use the download link in the email later.
Use the travel guide
When you buy the travel guide to Svalbard you get the book online so you can have it on your phone, tablet or computer – and of course you can choose to print it. Use the maps and tour suggestions and you will have a good and content-rich journey.

This construction is one of the most distinctive and characteristic buildings in Longyearbyen. During its operation, the junction served as a gathering point for the coal coming from various mines around the city.
At this fine museum you can explore the exciting and dramatic expeditions that, with airships, departed from Svalbard towards the North Pole. These are the ships America in 1906-1909, Norway in 1926 and Italy in 1928.

Svalbard Church was built and serves as a church for all residents of the archipelago, and people from, for example, Barentsburg and Sveagruva are also always welcome here. The present church was inaugurated in 1958.
The University Centre in Svalbard is a public university founded in 1993 by the Norwegian state. The idea of a university was to offer higher education in Arctic science.
Similar to Svalbard Travel Guide
There are no listings matching your search.
Reset